200 Quiz
Question 1 of 215
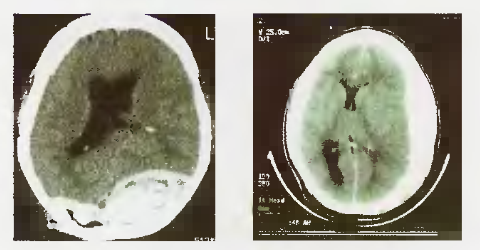
What do the two images depict (left shows lens shape, right shows crescent shape)?

When is a non-contrast head CT scan considered the best initial imaging test?
In the context of head trauma and intracranial bleeding (epidural/subdural hematomas), what is the most accurate imaging test?
What imaging modality is shown in these images?
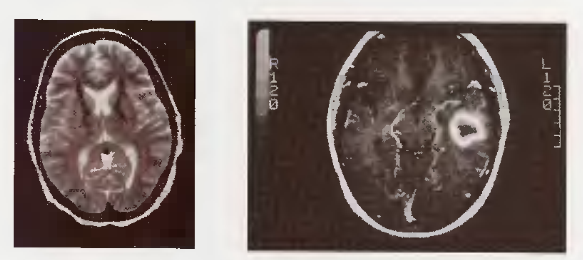
What does the image on the right show, compared to the normal image on the left?

For which neurological conditions is MRI considered the most accurate imaging test?
What is generally considered the only diagnostic procedure more accurate than an MRI for a suspected brain mass lesion?
What are Anti-Acetylcholine Receptor (Anti-Ach-R) Antibodies?
When are Anti-Acetylcholine Receptor (Anti-Ach-R) Antibodies considered the best initial test?
What diagnostic test is considered the most sensitive (more accurate than Anti-Ach-R antibodies) for Myasthenia Gravis?
What is Carotid Doppler?
When is ordering a Carotid Doppler indicated?
What is considered the most accurate diagnostic test for evaluating carotid artery stenosis?
When is a Cervical Spine X-ray indicated based on the mechanism of injury described?
What is a CT Myelogram primarily used to detect?
How is a CT Myelogram performed?
Why is CT Myelogram rarely performed today and often considered a wrong answer on exams?
What is the Edrophonium (Tensilon) Test?
How does the Edrophonium (Tensilon) Test work?
When is the Edrophonium (Tensilon) Test indicated?
What is considered the single most accurate diagnostic test for Myasthenia Gravis?
What neoplasm is associated with Myasthenia Gravis in about 10% of cases?
What is an Electroencephalogram (EEG)?
When is an EEG the best answer as a diagnostic tool?
What type of EEG is considered the most sensitive, especially for evaluating if anti-epileptic therapy can be safely stopped?
What is Electromyography (EMG)?
How is EMG typically performed?
Seeing EMG mentioned in a case should prompt consideration of which group of diseases?
For which condition is Single-Fiber EMG considered the single most accurate diagnostic test?
For which condition is combined EMG and Nerve Conduction Velocity (NCV) testing the single most accurate test?
What is a Lumbar Puncture (LP)?
In which scenarios is performing a Lumbar Puncture (LP) indicated?
When is performing a Lumbar Puncture (LP) contraindicated without first obtaining a head CT scan?
What are Oligoclonal Bands?
The presence of Oligoclonal Bands in CSF is suggestive, though not specific, for which neurological condition?
When is testing CSF for Oligoclonal Bands typically recommended in the evaluation of possible Multiple Sclerosis (MS)?
What is considered the most accurate test for diagnosing Multiple Sclerosis (MS)?
What is the Urea Breath Test?
When is the Urea Breath Test most appropriately used in the management of H. pylori infection?
In which clinical scenario would a Urea Breath Test be indicated?
What is Serum Trypsinogen concentration used to assess?
What level of Serum Trypsinogen would be expected in steatorrhea caused by chronic pancreatitis?
When is measuring Serum Trypsinogen level indicated?
What is Fasting Transferrin Saturation?
Measuring Fasting Transferrin Saturation is considered the best initial test for diagnosing which condition?
When should testing for Fasting Transferrin Saturation be considered?
If Fasting Transferrin Saturation is elevated, suggesting Hereditary Hemochromatosis, what is the most accurate confirmatory test?
What is the underlying pathogenesis of Hereditary Hemochromatosis?
What is the optimal age range for screening family members of patients with Hereditary Hemochromatosis?
What is the Sudan Black stain used for in stool analysis?
What is considered the most accurate test for quantifying fat malabsorption, although rarely performed?
When is ordering a Sudan Black stain of stool indicated?
What was the String Test historically used for?
Why is the String Test considered obsolete and always a wrong answer on modern exams?
What is the 72-Hour Fecal Fat collection test used for?
When might the 72-Hour Fecal Fat test be considered (despite usually being the wrong answer)?
In which patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) should screening upper endoscopy be considered?
What is the recommended management and surveillance for Barrett's esophagus found on screening endoscopy?
What is the Secretin Stimulation Test used for?
How does the Secretin Stimulation Test help diagnose Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome (ZES)?
How does the Secretin Stimulation Test help diagnose Chronic Pancreatitis?
When is the Secretin Stimulation Test indicated for suspected Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome (ZES)?
What is 24-Hour Esophageal pH Monitoring used for?
In which clinical scenarios is 24-Hour Esophageal pH Monitoring the appropriate test?
What diagnostic test involves PAS (Periodic acid-Schiff) staining of a small bowel biopsy specimen?
When should PAS staining of a small bowel biopsy be considered for diagnosing Whipple's disease?
What is the recommended treatment for Whipple's disease?
What is a HIDA (Hepatobiliary Iminodiacetic Acid) Scan used for?
When is a HIDA scan indicated?
How does a HIDA scan work, and what finding suggests acute cholecystitis?
When is a HIDA scan often considered the wrong answer or unnecessary?
What genetic tests are used as confirmatory tests for hereditary hemochromatosis?
When is genetic testing for HFE mutations (like C282Y) indicated?
What is Gastrograffin?
When is Gastrograffin the contrast agent of choice for diagnostic imaging?
What is the most accurate imaging test for confirming suspected esophageal perforation (Boerhaave's syndrome)?
What is the significance of measuring serum Gastrin levels?
When is measuring serum Gastrin level the best initial test?
If the fasting serum Gastrin level is elevated but not definitively diagnostic for ZES, what additional test can help confirm the diagnosis?
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome (ZES) is often associated with which genetic syndrome?
What is the purpose of testing stool for Fecal Leukocytes?
The presence of Fecal Leukocytes in stool suggests diarrhea caused by which type of pathogens?
When is testing for Fecal Leukocytes indicated?
What is Fecal Occult Blood Testing (FOBT)?
When is Fecal Occult Blood Testing (FOBT) primarily used?
If a Fecal Occult Blood Test (FOBT) is positive, what is the recommended follow-up investigation?
What is Esophageal Manometry used to diagnose?
How is Esophageal Manometry performed?
When is Esophageal Manometry indicated?
What is Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)?
For which conditions is ERCP considered the most accurate diagnostic test (and often therapeutic)?
What is the characteristic appearance of Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) on ERCP?
When is ERCP most strongly indicated?
What is the D-Xylose test used for?
How does the D-Xylose test work?
When is the D-Xylose test indicated?
What is generally considered the most accurate test for assessing the small bowel mucosa when malabsorption is suspected?
In which malabsorptive conditions would the D-Xylose test likely be abnormal (low urinary excretion)?
What are the standard colonoscopy screening recommendations for the general population?
How do colonoscopy screening recommendations change for an individual with a single first-degree relative diagnosed with colon cancer?
What are the colonoscopy screening recommendations for individuals with Hereditary Non-Polyposis Cancer Syndrome (HNPCC or Lynch Syndrome)?
What is Ceruloplasmin?
Measuring serum Ceruloplasmin levels (along with slit-lamp exam for Kayser-Fleischer rings) is the best initial approach for diagnosing which condition?
When should testing for Ceruloplasmin be considered?
Is a high or low serum Ceruloplasmin level typically considered strong evidence for Wilson's Disease?
What additional tests help confirm the diagnosis of Wilson's Disease?
What is a Bleeding Scan (Technetium-labeled RBC scan)?
When is a Bleeding Scan indicated?
What is the Bernstein Test?
How is the Bernstein Test performed?
Is the Bernstein Test considered a current or recommended diagnostic test for GERD?
For which symptom is a Barium Esophagram (Barium Swallow) generally the best initial test (unless obstruction is obvious)?
What characteristic findings might be seen on a Barium Esophagram in Achalasia and Diffuse Esophageal Spasm?
For which esophageal conditions is the Barium Esophagram considered the most accurate diagnostic test?
If a Barium Esophagram suggests a motility disorder (achalasia, spasm) or cancer, what is the most accurate follow-up test?
What condition is suggested by the presence of Anti-Smooth Muscle Antibodies (ASMA)?
When should testing for Anti-Smooth Muscle Antibodies (ASMA) be considered?
Besides ASMA, what other immune markers are often associated with Autoimmune Hepatitis?
What is considered the most accurate test for definitively diagnosing Autoimmune Hepatitis?
What is the primary diagnostic utility of testing for Anti-Mitochondrial Antibodies (AMA)?
When should testing for Anti-Mitochondrial Antibodies (AMA) be performed?
What is the most accurate test for confirming the diagnosis of Primary Biliary Cirrhosis (PBC)?
What is Capsule Endoscopy?
When is Capsule Endoscopy the procedure of choice?
What are Anti-endomysial and Anti-gliadin Antibodies?
When is testing for Anti-endomysial and Anti-gliadin Antibodies indicated?
What is considered the most accurate test for definitively diagnosing Celiac Disease?
What conditions can a Barium Enema (BE) potentially detect?
What is the generally preferred follow-up test if a Barium Enema reveals a suspicious lesion in the colon?
In which situations is performing a Barium Enema contraindicated?
What specific abnormalities are shown in the left and right images of the Barium Enema?

Is Barium Enema ever considered the 'most accurate test' if colonoscopy is available as an option?
What condition is shown in the upper endoscopy image, characterized by metaplastic columnar epithelium replacing squamous epithelium in the distal esophagus?
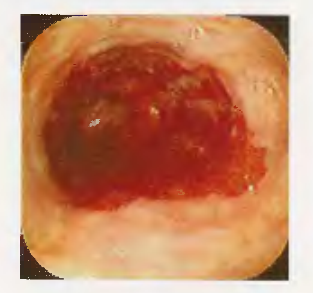
What is the underlying pathophysiology of Barrett's esophagus?
What are the potential complications of Barrett's esophagus?
What study is shown in the image?
